How Food, Exercise and Sleep Hygiene Impact Your Circadian Rhythm
Share
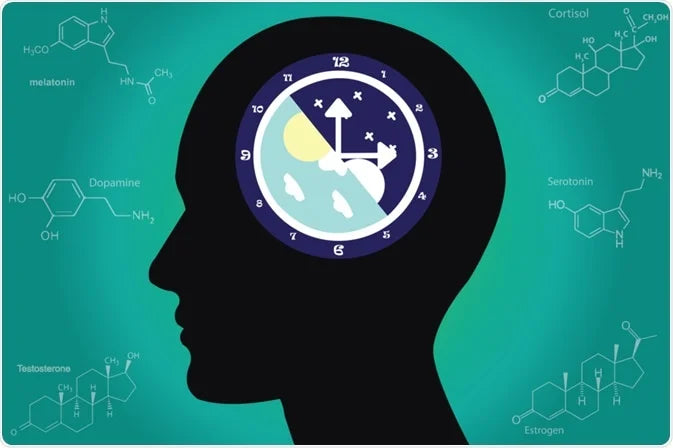
The circadian rhythm is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. Various factors, including food, exercise, and sleep hygiene, play crucial roles in influencing the circadian rhythm.
1. Food and Circadian Rhythm:
- Meal Timing: Eating at consistent times each day helps regulate the circadian rhythm. Irregular meal times can disrupt the body's internal clock.
- Light Exposure: Exposure to natural light during the day and avoiding bright light in the evening can help synchronize the circadian rhythm. Light influences the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: Limit the intake of caffeine and alcohol, especially in the evening. Both substances can interfere with sleep patterns.
2. Exercise and Circadian Rhythm:
- Morning Exercise: Engaging in physical activity in the morning can help regulate the circadian rhythm and improve overall sleep quality.
- Avoid Intense Exercise Before Bed: Vigorous exercise close to bedtime may temporarily increase alertness and interfere with the ability to fall asleep. Aim to finish intense workouts at least a few hours before bedtime.
- Consistent Exercise Routine: Regular physical activity contributes to a more stable circadian rhythm.
Contact us for for Exercise recommendations based on your goals
3. Sleep Hygiene and Circadian Rhythm:
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, helps regulate the circadian rhythm.
- Bedtime Routine: Establishing a calming pre-sleep routine signals to the body that it's time to wind down. This might include activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques.
- Limit Exposure to Screens: The blue light emitted by screens (phones, tablets, computers) can interfere with melatonin production. Try to limit screen time at least an hour before bedtime.
4. Nutrition and Sleep Quality:
- Balanced Diet: A well-balanced diet with sufficient nutrients supports overall health, including sleep. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet.
Check your body nutrition need using our Nutrition and Calories Calculator
Contact us for for daily balanced meals recommendations based on your goals
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Large or heavy meals close to bedtime may cause discomfort and indigestion, affecting sleep quality.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is important, but try to limit excessive fluid intake close to bedtime to avoid disruptive trips to the bathroom during the night.
- Nutrient Timing: Some nutrients, like carbohydrates, may have a calming effect and can be consumed in the evening to promote relaxation.
5. Additional Tips:
- Mind-Body Practices: Practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can promote relaxation and contribute to better sleep.
- Temperature Control: Keep the bedroom cool, quiet, and dark. A comfortable sleeping environment supports a healthy sleep-wake cycle.
Understanding the interconnectedness of food, exercise, and sleep hygiene is essential for maintaining a well-functioning circadian rhythm. Implementing healthy habits in each of these areas contributes to better sleep quality and overall well-being. If sleep issues persist, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Contact us for for professional for personalized guidance
